Approved by
Chief Medical Officer of
Municipal Hospital No.4
(Municipal Budgetary Healthcare Facility)
M.E. Povkh
December 15, 2011
Report on
“Clinical Benefit Assessment of ALMAG-03 Device During Treatment of Brain Diseases”
Acute cerebrovascular accidents are among the most common pathological conditions in neurological practice, and clinical medicine as a whole. According to the World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies, at least 15 million of strokes are registered worldwide every year. Moreover, it is assumed that this data is clearly underestimated, since in the developing countries many cases of stroke are either not registered or receive no medical attendance whatsoever due to inaccessibility of health care. In Russia, annual incidence of stroke is 3.4 per 1,000 people. This equals to over 450,000 new strokes annually in absolute terms.
The most common risk factor for stroke is arterial hypertension, which is detected in 72% of cases of stroke. It can thus be stated that the fatality risk after stroke increases with the very presence of hypertension and particularly weak commitment to its treatment. The second most frequent risk factor is attributed to heart diseases (41%). This group of diseases is diverse and includes acute and chronic forms of coronary artery disease, valvular heart diseases of rheumatic and atherosclerotic origin, endocardial, myocardial and pericardial diseases. The other frequently prevailing factors include stress, diabetes and dyslipidemia (14.3%, 14.2% and 14.0% respectively), the three of these having no significant differences among one another.
The expected positive outcome of stroke (apart from early spontaneous recovery of functions) is to a large extent determined by an early start of rehabilitation procedures and their adequacy, as well as preservation of the patient’s intelligence and activity.
The main rehabilitation principles include:
- early start;
- consistency and durability which can be ensured only through a well-organized step-by-step rehabilitation system;
- comprehensiveness and adequacy;
- active involvement of the patients themselves and their family members in the rehabilitation process.
In terms of restoration of functions and for rehabilitation purposes, the time after stroke is divided into four periods:
- acute period (the first 3-4 months);
- early recovery period (the first 6 months, of which the first 3 months play the major role for gain of motion);
- late recovery period (6 months to 1 year);
- residual period (1 year and later on).
Rehabilitation activities in the acute period of stroke are aimed at achieving the following:
- elimination of brain edema;
- improvement of blood circulation in the areas surrounding the lesion;
- disinhibition of functionally inactive (“shut-off”), but morphologically intact neurons (reversal of diaschisis);
- enhancement of the body’s adaptation mechanisms and prevention of major diseases that had previously led to stroke progression (hypertension, heart diseases).
In view of the above, transcranial magnetic therapy appears to be of appropriate use as part of complex treatment because the biophysical mechanism of its action corresponds to the objectives described.
An assessment study of performance characteristics and effectiveness of the methods specified in the instructions for medical use of ALMAG-03 magneto-therapy device manufactured by Yelatma Instrument Making Enterprise JSC has been conducted at neurology departments No. 1, 2, 3, 4 between November 1, 2011 and December 6, 2011.
To execute the above study, the following items have been submitted:
- two pilot samples of ALMAG-03 device (GIKS.106) that have passed the required warranty tests;
- operating manual for ALMAG-03 device (GIKS.106 OM);
- toxicological statement No.011 dd. 14/11/2011;
- draft instructions for medical use.
ALMAG-03 device consists of a control unit and a “headband”-type emitter. The “headband” emitter consists of two flexible emitting lines. Each of the lines contains 6 individual inductors (emitters). ALMAG-03 generates two types of pulsed magnetic field, “travelling” and “static”.
The following exposure programs of the device have been designed for treatment of brain diseases and hypertensive disease:
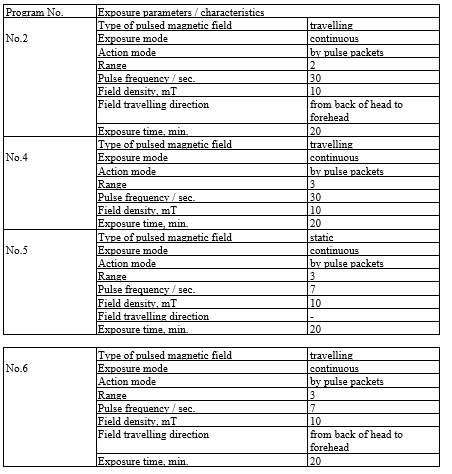
The device has been used for treatment as follows:
- vascular encephalopathy: 14 patients;
- hypertensive disease (concomitant condition): 15 patients;
- acute ischemic stroke of various sites: 14 patients;
- after-effects of cerebrovascular accidents: 10 patients;
- transient ischemic attack: 10 patients;
- arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (concomitant condition): 10 patients;
- toxic encephalopathy: 5 patients;
- migraine: 5 patients;
- cervical osteochondrosis (concomitant condition): 9 patients
in accordance with the methods described in the instructions for medical use.
Patients’ subjective complaints have been taken into account during treatment, and monitoring of treatment effectiveness has been conducted based on unspecific adaptation mechanisms:
- BP level;
- pulse rate;
- pulse oximetry data;
- blood tests for: INR, prothrombin index, aPTT, fibrinogen;
Anxiety level self-assessment based on Spielberger-Hanin scale has been performed.
In the process of treatment of vascular encephalopathy, acute ischemic stroke of various sites, after-effects of cerebrovascular accidents, transient ischemic attack, toxic encephalopathy, migraine, as well as concomitant conditions, such as hypertensive disease, arteriosclerotic encephalopathy, cervical osteochondrosis, the nature of patients’ complaints has changed. At the beginning of treatment, 100% of patients had complained of sleep disorders and headaches, 95% of irritability. Upon course completion, the following results have been registered:
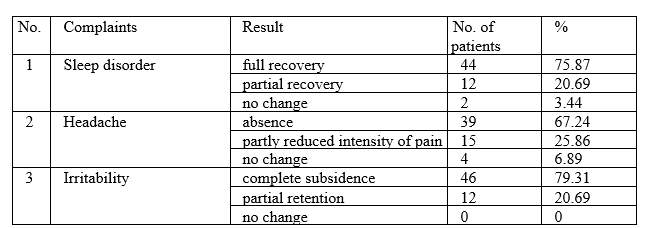
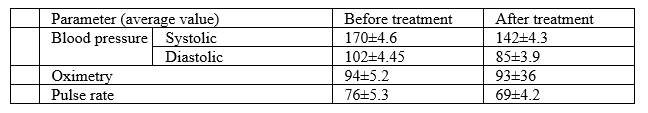
As related to cardiovascular system, the following have been observed:
As related to blood coagulation (INR, PTI, aPTT, fibrinogen), normalization of parameter values has been observed.
Based on data obtained on Spielberger-Hanin scale, anxiety level has changed as follows:
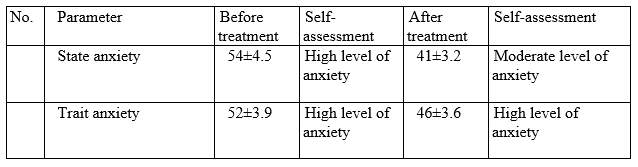
Conclusion.
The instructions for medical use of ALMAG-03 device are written in a manner and terminology which are easily understood by healthcare professionals and allow them to quickly master the use of the device. Application methods are simple and do not require additional training of medical personnel.
In the course of ALMAG-03 device application, positive subjective and objective changes have been detected in the organisms of patients suffering from brain diseases and concomitant conditions of the cardiovascular system. Exposure to pulsed magnetic fields generated by ALMAG-03 device promoted improvement of general well-being of patients. Improvement of sleep quality, subsidence or reduction in intensity of headaches and irritability has been recorded.
As related to cardiovascular system, a positive trend towards lowering of blood pressure has been observed. Positive aspects of pulse oximetry application have been noted, which allows to evaluate effectiveness of magneto-therapy action directly at patient’s bedside. The pulse oximetry data have demonstrated a reduction of blood oxygen content, which indicates an improvement in its uptake and activation of metabolic processes in the body. As related to blood coagulation system, normalization of parameter values has been observed, which is an important factor in disease prognosis and prevention of recurrent strokes.
ALMAG-03 device is useful in cases of hypertensive disease and hypertensive encephalopathy, after-effects of cerebrovascular accidents, transient ischemic attack, chronic cerebral ischemia, arteriosclerotic and toxic encephalopathy, migraine, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with symptoms of cephalalgia. Device application is also indicated in case of sleep problems.
Contraindications against use of ALMAG-03 device include heavy cardiac arrhythmias with heart failures, respiratory disturbances, acute purulent processes in the head and neck, fever of any origin, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhages and coagulopathies.
ALMAG-03 device designed for treatment of cerebral diseases of various natures is appropriate for use in medical practice for treatment and prevention of brain diseases.
Head of Physiotherapy Department, Physical Therapist
S.P. Pupina
Chief Independent Expert, Physiotherapist of the Department
of Health of the Vladimir Region, Physical Therapist
L.A. Chernyavskaya
