Ministry of Healthcare of the Astrakhan Region
State Budgetary Healthcare Facility of the Astrakhan Region
Municipal Polyclinic No.4
<Logo> /Municipal Polyclinic No.4/
TIN 3018317420
26 Silikatnaya St.
Astrakhan 414013
Phone/fax: 31-77-33
e-mail: muzgp10@rambler.ru
Dated 10/04/2014 No. 01-10-105711
Application of Magnetic Field in Complex Treatment of
Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease which has for decades been the focus of rheumatologists’ attention all over the world. This is explained by major medical and social significance of the disease. Its prevalence reaches 0.5-2% of total population in developed countries. Rheumatoid arthritis patients are prone to a 3 to 7 years’ shorter life expectancy as compared to the overall population. The damage caused by this disease to the society is enormous due to early disability of patients, which can occur in the first 5 years from the disease onset, in case if its active treatment has not been started in good time.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease of unclear origin, which is characterized by damage of peripheral synovial joints and periarticular tissues, accompanied by autoimmune disorders and possibly leading to destruction of articular cartilage and bone, as well as to systemic inflammatory changes.
The purpose of the study is to evaluate the possibility of enhancing the effectiveness of complex therapy of rheumatoid arthritis by including exposure to pulsed magnetic field produced by “Almag-02” device as part of the therapeutic process.
Materials and Methods
Work had been conducted over a 2-year period between 2010 and 2012. In this period, 62 patients suffering from RA were under medical supervision. The diagnosis was verified in accordance with the American Rheumatism Association criteria. The clinical profile of the patients is presented in Table 1.
Among the surveyed individuals, female patients prevailed, who had RA of second degree of activity, radiographic stage II-III, accompanied by joints insufficiency (JI) of degrees I-II.
All participants of the study were divided into 2 groups: treatment one (36 patients) and control one (26 patients). Magneto-therapy within the treatment group was conducted in line with background therapy. During the study, the dosage of disease-modifying drugs was not changed, and no intra-articular administration of glucocorticoids was performed. The last intra-articular administration of glucocorticoids was allowed not less than one month prior to initial engagement in the study.
Magneto-therapy procedures with “Almag-02” device were provided once a day within 12-day period as follows: The main emitter was placed over the adrenal glands projection area, and the affected joint was wrapped with the flexible emitting line. Both emitters were positioned with their north polarity sides adjacent to the body. Field density: 10 mT (main emitter) and 6 mT (flexible emitting line); frequency: 100 Hz and 16 Hz respectively. Procedure duration: 10 minutes. Exposure of two joints within a single procedure was allowed; in that case, the exposure time was 10 minutes for each joint. The patients of the control group were receiving only background therapy.
Table 1. Clinical profile of RA patients
| Parameters |
Patient groups |
|
|
Treatment group (n=36) |
Control group (n=26) |
|
| Gender (m/f) |
13:23 |
10:16 |
| Age (years) |
28-57 |
25-59 |
| Median age (years) |
52.4±3.8 |
51.8±4.6 |
| Average disease duration (years) |
5.9±0.7 |
6.9±1.1 |
| Radiographic stage: | ||
| ІІ |
17 |
11 |
| ІІІ |
19 |
15 |
| JI degree: | ||
| І |
13 |
10 |
| ІІ |
23 |
16 |
The patient groups were comparable in terms of their ages, disease duration and severity (all р>0.05). All patients were subjected to physical examination, laboratory tests, X-ray examination of the joints of hands and feet to clarify RA stage.
The criteria for withdrawal from the study were: cardiovascular insufficiency, severe hepatic and renal impairments, pregnancy and lactation.
The treatment was conducted in line with background therapy. During the study, the dosage of disease-modifying drugs was not changed, and no intra-articular administration of glucocorticoids was performed. The last intra-articular administration of glucocorticoids was allowed not less than one month prior to initial engagement in the study.
The change patterns of a patient’s condition were traced on the basis of standard clinical criteria: duration of morning stiffness (in minutes); pain level at rest, on movement, and at night-time (on a 10-point visual analogue scale, VAS); number of painful and inflamed joints; range of motions in the affected joints. The patient and the doctor evaluated treatment effectiveness based on the following 4-point scale: 0 – no effect; 1 – insufficiently notable effect; 2 – favorable; 3 – good; 4 – excellent. To assess the inflammatory process intensity, the following laboratory parameters were used: ESR, C-reactive protein level, RBC count, Hb level. To monitor possible toxic impact of the medication on the liver and kidneys, the levels of transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, creatinine, urea were determined, and clinical urine analysis was performed. The clinical and laboratory parameters were assessed at baseline and upon completion of the 15-day-long treatment course.
The results obtained, and their discussion
Analysis of the treatment results demonstrates a positive analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of magneto-therapy for most clinical observations. In the course of the treatment, duration of morning stiffness within the treatment group of patients decreased by 60.6% (89.9±17,3 min. and 35.4±16.8 min. respectively), within the control group by 55% (93.5±17.8 min. and 42.1±18.2 min. respectively) (all p <0.05).
Reduction of the pain severity as per VAS for at least 50% at rest in the treatment group was detected in 25 patients (69.4%); in the control group in 14 patients (53.8%); on movement: in 21 (58.3%) and 11 (42.3%) patients respectively; at night hours: in 27 (75.0%) and 11 (42.3%) patients respectively.
On the background of the therapy, a significant decrease in the number of painful joints was observed in the treatment group in 22 patients (61.1%), and in the control group in 13 patients (50%). The anti-inflammatory effect of magneto-therapy was expressed by a positive reduction of the number of inflamed joints: in 26 (66.6%) and 14 (53.8%) patients respectively. An increase in the range of active motions in the affected joints was observed in 27 (75.0%) and 19 (73.0%) patients respectively.
Within the laboratory parameters, ESR and C-reactive protein values were significantly reduced by the end of the study: in the treatment group, 15 such patients (41.6%) were registered, in the control group, 12 patients (46.1%); the rest did not demonstrate any consistent improvements. Hemoglobin level remained within the normal range, as well as the liver and kidneys functional indicators.
During the study, none of the patients of any group had any relapses of joint synovitis. Usage of magneto-therapy did not cause any side effects. In the control group, the side effects in the form of gastralgias were observed in 3 patients (11.5%), who switched to other NSAIDs after prescription of gastroprotectors.
The treatment effectiveness assessments by patient and by doctor (Diagram 1) nearly coincided for all groups.
Diagram 1. Treatment effectiveness assessment by patient and by doctor
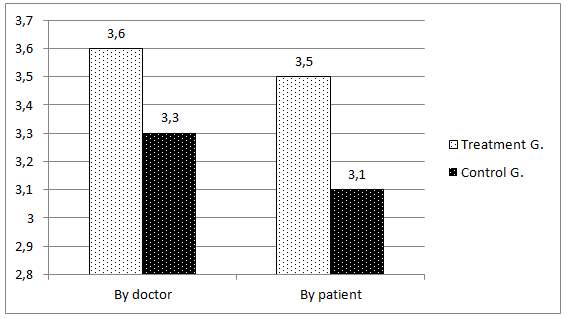
The highest effectiveness value was in the treatment group, which proves the effectiveness and safety of using magneto-therapy with “traveling” magnetic field as part of complex treatment of this group of patients. The most notable effects observed during application of magnetic field as part of complex treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients include the anti-inflammatory action (reduction of the pain syndrome intensity) and, to a lesser extent, the improvement of the functional state of joints.
The above findings indicate the clinical efficacy and safety of magneto-therapy with low-frequency “traveling” magnetic field of “Almag-02” device for treatment of RA patients. The ease of the device usage promotes its large-scale introduction into medical practice at all stages of care for rheumatoid arthritis patients.
